Inflammation is a natural bodily response to injury or infection. Inflammatory cells are responsible for attacking bacteria or toxins that would otherwise slow down one’s healing process as well as contribute to more serious health conditions (1). While inflammation is a necessary reaction, two distinct types of inflammation can affect individuals; acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is the normal bodily response over a short period of time, while chronic inflammation refers to persistent inflammatory attacks long after threats have been eliminated.
The process of long-term inflammation can cause severe damage to the joints and muscles, and this article aims to share how to prevent you from developing chronic inflammation. Below, we outline the best foods that fight inflammation and how to manage symptoms.
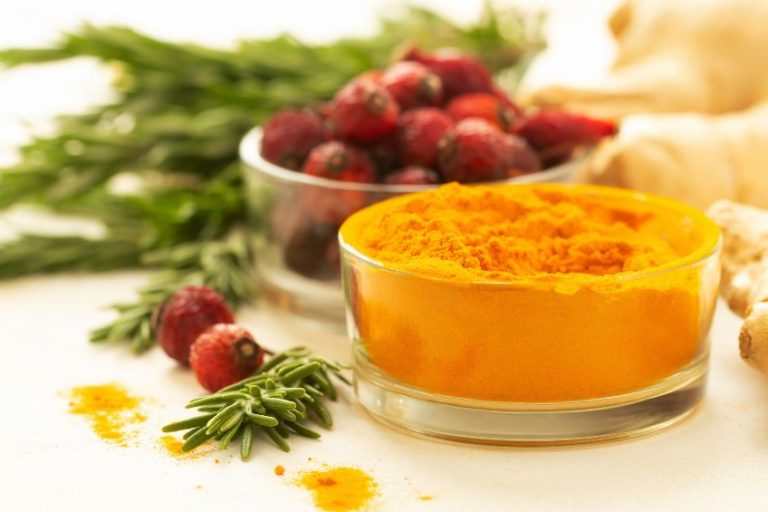
Turmeric
The popular household spice offers more nutritional value than you may have originally thought. Besides being a great addition to curry and other spicy dishes, turmeric provides plenty of health benefits because of the spice’s biochemical makeup. Most notably, turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory that is scientifically linked to the benefits of consuming turmeric. Studies have assessed the potential for curcumin, when combined with piperine, to reduce inflammation among individuals suffering from metabolic syndrome. One particular study concluded that these individuals experienced a substantial decrease in the inflammatory marker CRP (2).
Consuming curcumin as a byproduct of using the turmeric spice in your dishes may, however, not provide enough of the key ingredient for similar results. For this reason, individuals turn to turmeric curcumin supplements, like Research Verified® Turmeric Curcumin, that provide an effective concentration of the core ingredient combined with BioPerine®, a powerful patented variation of piperine, shown to increase absorption by 2000%!
Avocados
Often referred to as “green gold”, avocados have become a staple addition to the best diets, such as the Mediterranean diet, because of their potential health benefits and delicious texture. Avocados contain high levels of magnesium, fiber, potassium, and monounsaturated fats. The combination of these nutrients, according to authoritative sources, provides the body with antioxidants responsible for controlling weight gain (3).
Furthermore, reports claim that avocado can reduce inflammation in the skin and promote the generation of new skin cells (4). One study highlighted the food’s particular ability to reduce inflammatory markers interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and CRP (5).
Berries
Berries are another category of food that contain essential vitamins and minerals, as well as high concentrations of fiber. Below, we list some of the most popular and beneficial berries to include in your healthy diet:
- Blueberries
- Raspberries
- Strawberries
The primary anti-inflammatory properties of berries are linked to the antioxidants present in the foods, anthocyanins. According to reports, these antioxidants play a vital role in the reduction of toxins and bacteria that could lead to serious health conditions as a result of long-term exposure to inflammation. One particular study found that blueberry powder was an effective means of increasing natural killer cells (NK cells) that help the body’s immune system function properly (6).
Based on these scientific reports, one can conclude that a combination of a healthy diet including berries and berry-based powders or supplements will deliver significant anti-inflammatory benefits.
Fatty Fish
Don’t let the word “fatty” deter you from including fatty fish in your diet as these foods provide the body with healthy fats necessary for reducing inflammation and fighting weight gain. Furthermore, fatty fish is one of the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
These two compounds play a role in reducing inflammation and decreasing one’s likeliness of experiencing metabolic syndrome, kidney disease, and other serious health conditions. The reason for this is that the body metabolizes fatty acids to produce resolvins and protectins that are responsible for various anti-inflammatory effects. Furthermore, studies highlight the role that salmon consumption plays in the reduction of inflammatory markers CRP (7).
The most beneficial fish to consume include:
- Salmon
- Herring
- Anchovies
- Mackerel
- Sardines
Mushrooms
Modern researchers and scientists continue to turn to mushrooms as a source of healthy vitamins and nutrients necessary for various positive influences on the body. More recently, reports note the powerful anti-inflammatory properties of certain types of mushrooms, including:
- Truffles
- Portobello mushrooms
- Shiitake mushrooms
These foods are extremely low in calories, a healthy addition to any diet, and present high concentrations of crucial nutrients such as selenium, copper, and B vitamins. The phenols found in mushrooms are also reported to provide a natural source of anti-inflammatory properties (8). More specifically, studies highlight that lion’s mane, a type of mushroom, may prevent low-grade inflammation within those that suffer from obesity (9).
Some of the best supplements on the market include patented ingredients derived from various types of mushrooms. A combination of a healthy diet that includes mushroom-derived supplements and meals with raw or lightly-cooked mushrooms should deliver positive anti-inflammatory results.
BrocColi
Broccoli, along with other cruciferous vegetables like kale and cauliflower, is incredibly healthy as it contains a number of essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. Broccoli is most commonly known to provide the body with nutrients necessary for reducing the risk of heart disease (10). But, broccoli is even more beneficial than that.
Many note that broccoli’s ability to support the body and prevent diseases is linked to its anti-inflammatory properties. According to reports, broccoli’s high levels of sulforaphane are responsible for decreasing the development of cytokines and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), molecules that play a primary role in the body’s natural inflammatory response (11).
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are another nutritional food that provides the body with a variety of necessary nutrients, namely vitamin C, potassium, and lycopene. Lycopene is an essential antioxidant that is said to offer the body several anti-inflammatory benefits (12).
One of the roles that lycopene plays in the body is to target and eliminate the development of pro-inflammatory compounds. By doing so, lycopene can mitigate low-grade chronic inflammation and help individuals manage the symptoms of said inflammation (13). It is important to note that cooking tomatoes with olive oil can increase the rate at which one’s body absorbs lycopene from the popular food. This is due to the fact that lycopene is a carotenoid, a compound that is better absorbed with a type of fat source.
How to Manage Symptoms of Inflammation
A diet that includes the above-mentioned foods should contribute to a better inflammatory response as they provide nutrients and chemicals that promote proper inflammatory function. That said, the addition of targeted health supplements can aid the body’s inflammatory response over and above a well-balanced diet. Health supplements by Research Verified® are formulated to contain optimal concentrations of key ingredients with powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Combining the best foods for fighting inflammation along with anti-inflammatory may help manage inflammation and prevent the development of chronic inflammation in the future.
In CONLCUsion
A variety of foods contain essential vitamins, nutrients, and minerals that play healthy roles within the body. When it comes to inflammation and managing symptoms associated with chronic inflammation, individuals can add turmeric, avocados, berries, mushrooms, tomatoes, and more to their diets. Based on a number of studies, doing so alongside healthy lifestyle habits will help individuals manage their inflammation better and prevent the onset of more serious health conditions associated with chronic inflammation.